![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]()
Man made fish cribs are definitely worthwhile to fish providing cover and shelter for juvenile panfish and baitfish, Most cribs are built using hardwood logs strapped together and filled with branches. They attract all large game fish.The fishes world evolves around the ability to feed, reproduce and survive. Cover, Structure, Temperature and Oxygen are the key components. Understanding the waters of their world will help you determine the type of water and where they live.
Cover & Structure:These two terms are often confused as the same, but they are not. Cover is defined as a type of structure, natural or man made such as weeds, vegetation, fallen trees, docks, and swimming platforms. Structure is the physical characteristics of the water system; points, rock bars, islands, reefs, humps and breaklines. To understand the difference, if you completely drain the water only the structure will not move.
Breaklines & Edges![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]()
Courtesy of Fishing the North Country Publications
Anglers hearing or reading the phrases “fish caught off the first break” or “fish caught on the weed edge” may be confused as to their meaning. All active fish will relate to breaks or edges. Weed beds are like “aquatic neighborhoods” providing all stages of the food chain protection from predators or an ambush source for feeding. Breaklines (Breaks) are defined as an area of transition from one depth to another, one cover type to another, one water temperature to another, one water color to another, one substrate to another or any other transition that could influence fish behavior. Cover (weeds) next to a deep water breakline usually hold more fish than a shallow flat.
Humps and Reefs ![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]()
Courtesy of Fishing the North Country Publications
Any mid lake underwater structure higher than the surrounding area can be classified as a hump or reef, they are among the most productive structures in lakes and flowages. Walleye, smallmouth bass, northern pike and summer/autumn muskie are attractive possibilities. If weeds, boulders and ledges are present, this structure will be even better, producing more game fish.Points and Bars![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]()
Courtesy of Fishing the North Country Publications
Protruding shoreline points and bars offer a diversity in structure and are fish producers throughout the year. Key bottom components are, inside turns and drops offs. Add cover such as submergent and emergent weeds, drowned wood, brushpiles and manmade cribs and you have a top attraction for all gamefish. Wood and Weeds
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() Courtesy of Fishing the North Country PublicationsDrowned wood, laydowns, brush plies composed of fir, pine, oak and maple typically lasts for years. By contrast birch, aspen and popple provide cover for two to three years before decomposing to remnants. Drowned wood is terrific cover. The more complex the branches below the surface the better for fish. More branches more cover for a game fish to ambush prey. Finding “good” drowned wood means finding walleye, smallmouth bass and muskie.
Courtesy of Fishing the North Country PublicationsDrowned wood, laydowns, brush plies composed of fir, pine, oak and maple typically lasts for years. By contrast birch, aspen and popple provide cover for two to three years before decomposing to remnants. Drowned wood is terrific cover. The more complex the branches below the surface the better for fish. More branches more cover for a game fish to ambush prey. Finding “good” drowned wood means finding walleye, smallmouth bass and muskie. Weeds and weedline edges are important throughout the fishing season as they are used for spawning in spring; shelter, cover and foraging in summer/fall and feeding in winter for all game fish. Fishing the weeds always keep in mind the “cover within cover” principle – weed points, edges, deep weedlines, transitions from one weed species to the next, channels, clumps and inside turns among others.
Types of Weeds
The presence of aquatic plants is one of the best indicators of whether a lake or a stream will be a good producer of fish. Most aquatic life which fish feed upon requires these plants for food. Plants also provide a fishery with protective cover and life-giving oxygen. Aquatic plants are classified into floating, emergent, submerged and algae varieties as each type has slightly different features.Floating![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() Floating plants are not rooted and are free to move about the water’s surface. The main habitat for floating plants are backwater areas on rivers and streams where the current slackens and protected bays on lakes and flowages. In limited water movement area’s floating plants can be mixed in with other emergent and submerged plants forming what is commonly called “slop” by creating a surface mat that attracts largemouth bass, in deeper waters slop will hold northern pike and muskie. Fishing slop is extremely fun when the fish are on and you have the right set-up and lures. Fishing the slop requires heavy tackle and line to horse the fish out of cover. Baitcasting reels spooled with low stretch 17lb to 30lb test line, rods rated heavy with fast action are recommended. Lure choices include weedless soft plastics, worms and lizards using heavy sinkers to penetrate the thick vegetation, top water frog and rat imitations are excellent for surface slop fishing, there is nothing more exciting when a bass explodes on one of these. The common North American native floating plants are Duckweed, Bladderwort and Watermeal.
Floating plants are not rooted and are free to move about the water’s surface. The main habitat for floating plants are backwater areas on rivers and streams where the current slackens and protected bays on lakes and flowages. In limited water movement area’s floating plants can be mixed in with other emergent and submerged plants forming what is commonly called “slop” by creating a surface mat that attracts largemouth bass, in deeper waters slop will hold northern pike and muskie. Fishing slop is extremely fun when the fish are on and you have the right set-up and lures. Fishing the slop requires heavy tackle and line to horse the fish out of cover. Baitcasting reels spooled with low stretch 17lb to 30lb test line, rods rated heavy with fast action are recommended. Lure choices include weedless soft plastics, worms and lizards using heavy sinkers to penetrate the thick vegetation, top water frog and rat imitations are excellent for surface slop fishing, there is nothing more exciting when a bass explodes on one of these. The common North American native floating plants are Duckweed, Bladderwort and Watermeal.Emergent
An emergent plant are a rooted shallow water plant found along shorelines areas, which grows in the water but the stems stand above the surface. All emergent plants flower which allows the reproductive process through pollination by wind or by flying insects. Emergent plants provide an important function on the water’s edge that creates a network root system which resists erosion, where wave action and water flow might undercut banks and a barrier for shoreline sediment. These plants create habitat and food supply for many species of insect, fish, bird, and mammal. The most common North American emergent plants are Lily Pads, Bulrushes and Cattails.
White Water Lily Pads![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() The lily pad is a perennial flat leafed flowering rooted plant that grows in groups. For the most part they are found along shallower waters in sandy or soft bottomed areas. In clear water that can grow up to six to eight feet. The lily pad leaves are more rounded than heart shaped, bright green from 6-12 inches in diameter with a slit about the 1/3 of the leaf. The leaves float on the surface, the flower grow on separate stalks displaying brilliant white petals with a yellow center and are very fragrant. The flower opens each morning and closes as the sun goes down. A favorite habitat for largemouth bass. However many other species such as northern pike and muskies can be found in the lily pads as well.Bulrushes
The lily pad is a perennial flat leafed flowering rooted plant that grows in groups. For the most part they are found along shallower waters in sandy or soft bottomed areas. In clear water that can grow up to six to eight feet. The lily pad leaves are more rounded than heart shaped, bright green from 6-12 inches in diameter with a slit about the 1/3 of the leaf. The leaves float on the surface, the flower grow on separate stalks displaying brilliant white petals with a yellow center and are very fragrant. The flower opens each morning and closes as the sun goes down. A favorite habitat for largemouth bass. However many other species such as northern pike and muskies can be found in the lily pads as well.Bulrushes
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() There are several species of bulrushes known as reeds and pencil reeds. Bulrushes are perennial rooted grass-like plants and can grow to 10 feet tall in shallow water or in moist soils. Reeds generally grow on firm bottoms, bulrush grows in softer mud bottoms. The bulrush brownish flowers appears just below the tip of the stem. Reeds and bulrush provides excellent fish habitat and spawning areas for northern pike and, in early spring, provide nesting cover for largemouth bass and bluegills. Bulrushes attract marsh birds and songbirds. Seeds of bulrushes are consumed by ducks and other birds.
There are several species of bulrushes known as reeds and pencil reeds. Bulrushes are perennial rooted grass-like plants and can grow to 10 feet tall in shallow water or in moist soils. Reeds generally grow on firm bottoms, bulrush grows in softer mud bottoms. The bulrush brownish flowers appears just below the tip of the stem. Reeds and bulrush provides excellent fish habitat and spawning areas for northern pike and, in early spring, provide nesting cover for largemouth bass and bluegills. Bulrushes attract marsh birds and songbirds. Seeds of bulrushes are consumed by ducks and other birds.Cattails
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() Cattails are found in marshes, ditches, shorelines, shallow areas of lakes, ponds, and slow streams, quiet water up to 4 feet deep. They have slightly twisted rounded leaves, and can grow to 5 or 10 feet in height. Cattails are easily identified by their fuzzy brown cigar shaped flower (called the catkin) near the top of the stalk. Cattails spread rapidly when the catkin releases the seeds blowing in the wind or floating on the water’s surface. The cattail habitat helps stabilize marshy borders of lakes and ponds; helps protect shorelines from wave erosion; northern pike may spawn along shore behind the cattail fringe; provides cover and nesting sites for waterfowl and marsh birds such as the red-winged blackbird, stalks and roots are eaten by muskrats and beavers.
Cattails are found in marshes, ditches, shorelines, shallow areas of lakes, ponds, and slow streams, quiet water up to 4 feet deep. They have slightly twisted rounded leaves, and can grow to 5 or 10 feet in height. Cattails are easily identified by their fuzzy brown cigar shaped flower (called the catkin) near the top of the stalk. Cattails spread rapidly when the catkin releases the seeds blowing in the wind or floating on the water’s surface. The cattail habitat helps stabilize marshy borders of lakes and ponds; helps protect shorelines from wave erosion; northern pike may spawn along shore behind the cattail fringe; provides cover and nesting sites for waterfowl and marsh birds such as the red-winged blackbird, stalks and roots are eaten by muskrats and beavers. Submerged
Submerged plants are completely underwater and are generally rooted in the bottom sediment. If flowers exist, they may extend above the surface of the water. Submerged plants exchange carbon dioxide for dissolved oxygen during the periods of photosynthesis which provides a relatively stable source of oxygen for a water based ecosystem. Submerged weeds make up the majority of fishing cover (weed flats and weedlines) that will attract most all species walleye, bass, pike, muskie, trout and panfish. The submerged weed family consist of hundreds of species many introduced or exotic that grow prolifically and are considered to problematic in many lakes, rivers and streams. An example of this is Eurasian Watermilfoil Most fishing articles relating to weeds refer to names such as cabbage, coontail, and eel grass. The following information is a guide for identifying the most common submerged plants that will attract game fish.
Claspingleaf Pondweed (Cabbage)
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() This plant is known to anglers as cabbage and has over 50 varieties in North America. Cabbage is both a deep and shallow water weed that has broad leaves and a brittle stems. They vary in colors from brownish red called tobacco cabbage to a light green leaf. Cabbage is the preferred choice of many large game fish and the most productive. Cabbage is also known as pike weed, muskie weed, and celery.
This plant is known to anglers as cabbage and has over 50 varieties in North America. Cabbage is both a deep and shallow water weed that has broad leaves and a brittle stems. They vary in colors from brownish red called tobacco cabbage to a light green leaf. Cabbage is the preferred choice of many large game fish and the most productive. Cabbage is also known as pike weed, muskie weed, and celery. Coontail
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() Coontail or also know as hornwort, is a dark olive green bushy submerged perennial plant that grows in clumps or dense colonies that forms a canopy type cover in shallow water. The tips of branches are crowded with leaves giving it a “coontail” appearance. The submerged colonies of coontail provides excellent habitat and cover for bait fish as well as other wildlife species (e.g. amphibians, reptiles, ducks, etc.)which attracts most predator game fish. The fruits of coontail are consumed by ducks and it is considered a good wildlife food.
Coontail or also know as hornwort, is a dark olive green bushy submerged perennial plant that grows in clumps or dense colonies that forms a canopy type cover in shallow water. The tips of branches are crowded with leaves giving it a “coontail” appearance. The submerged colonies of coontail provides excellent habitat and cover for bait fish as well as other wildlife species (e.g. amphibians, reptiles, ducks, etc.)which attracts most predator game fish. The fruits of coontail are consumed by ducks and it is considered a good wildlife food. Eelgrass
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() Eelgrass is a rooted shallow water plant found in flowing water. It has long, thin, ribbon-like leaves (1/2 – 3/4 inches wide) that are commonly 3 to 4 feet long. The vein pattern in the leaves of eelgrass is very distinctive and resembles celery. Eelgrass forms dense colonies dominating other submerged plants to grow. The submerged portions of eel grass provides dense underwater structure as an excellent habitat for bait fish and invertebrates. Northern pike and bass favors eelgrass during the summer months. Other common names include: Tape grass and wild celery.
Eelgrass is a rooted shallow water plant found in flowing water. It has long, thin, ribbon-like leaves (1/2 – 3/4 inches wide) that are commonly 3 to 4 feet long. The vein pattern in the leaves of eelgrass is very distinctive and resembles celery. Eelgrass forms dense colonies dominating other submerged plants to grow. The submerged portions of eel grass provides dense underwater structure as an excellent habitat for bait fish and invertebrates. Northern pike and bass favors eelgrass during the summer months. Other common names include: Tape grass and wild celery. Elodea
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() Elodea is a rooted multi-branched perennial submerged plant that grows in cool fertile water to depths of approximately 10 feet. It is identified by its deep green color with 3 to 4 leaves attached directly to the stem. This weed develops quickly and provides good early season action, it attracts bait fish and bass along with other large game fish. Elodea has no known direct food value to wildlife but is used extensively by insects and invertebrates. Other common names include: Waterweed and walleye weed.
Elodea is a rooted multi-branched perennial submerged plant that grows in cool fertile water to depths of approximately 10 feet. It is identified by its deep green color with 3 to 4 leaves attached directly to the stem. This weed develops quickly and provides good early season action, it attracts bait fish and bass along with other large game fish. Elodea has no known direct food value to wildlife but is used extensively by insects and invertebrates. Other common names include: Waterweed and walleye weed.Cabomba![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]()
Cabomba also know as Fanwort is a long stemmed multi-branched submerged perennial plant similar to coontail and milfoil. It grows in tight beds over large areas, growing to within a foot of the surface. Because of it’s dense cover it provides habitats for micro invertebrates which in turn are used as food by bait fish and other wildlife species. Cabomba has little known direct food value to wildlife Eurasian Watermilfoil![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]()
Eurasian watermilfoil is a perennial submerged plant native to Europe, Asia, and Africa. It was introduced into the United States in the late 1800′s through the Aquarium Trade. Spread westward into inland lakes primarily by boats and also by waterbirds, it reached Midwestern states between the 1950s and 1980s. Today it is considered one of the most aggressive and invasive plants in the U.S. because of the dense colonies which it forms. This dense floating canopy will inhibit important native plants from growing. In shallow areas the Eurasian watermilfoil can interfere with water recreation such as boating, fishing, and swimming as well. Eurasian watermilfoil can spread from seeds or by fragmentation (A single segment of stem) that can take root and form a new colony. Fragments clinging to boats and trailers can spread the plant from lake to lake. Eurasian watermilfoil is a non-native and should not be spread.Algae
Algae are a basic water plant, some are composed of tiny single cells that float or suspend in the water giving a green, brown, or at times a red color to the water known as “bloom.” Others are multi celled that forms a thin and stringy or hair-like dark green slime commonly know as pond scum. While still others resemble submerged plants but without a true root system this is known as sandgrass. Algae although primitive, provides benefits to water systems by stabilizing bottom sediments and giving cover for small animals such as aquatic insects, snails, and scuds, which are valuable fish food.Planktonic![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]()
Planktonic algae, are floating microscopic single celled plants usually existing suspended in the upper few feet of water often reaching bloom proportions during the summer months based on temperature, light, nutrients making the water appear brownish or pea soup green.Filamentous
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() Filamentous algae are multi-celled that form into a mat of long chains or threads called filaments that resembles wet wool. Filamentous algae starts growing along the bottom in shallow water appearing fur-like, attaching to rocks, drowned wood, and other aquatic plants. As the production of oxygen increases it will float to the surface forming large mats, known as “Pond Scum.” Filamentous algae has no direct food value to wildlife.
Filamentous algae are multi-celled that form into a mat of long chains or threads called filaments that resembles wet wool. Filamentous algae starts growing along the bottom in shallow water appearing fur-like, attaching to rocks, drowned wood, and other aquatic plants. As the production of oxygen increases it will float to the surface forming large mats, known as “Pond Scum.” Filamentous algae has no direct food value to wildlife.Chara (Sandgrass)
![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]() Chara is the most advanced plant of the algae family though often confused with submerged plants. Chara commonly know as “sandgrass” is gray-green, branched with no root system, it grows in short thick mats, covering the lake bottom like a carpet. It can grow to depths of 30 feet, but is more common in shallower water. The stems/branches are brittle and hollow with rough ends, when crushed it emits a foul musty garlic like odor, often why it is called muskgrass or skunkweed. Sandgrass is beneficial promoting water clarity and lake bottom stabilization. During the mid summer through fall, walleyes and perch will be found on sandgrass flats.
Chara is the most advanced plant of the algae family though often confused with submerged plants. Chara commonly know as “sandgrass” is gray-green, branched with no root system, it grows in short thick mats, covering the lake bottom like a carpet. It can grow to depths of 30 feet, but is more common in shallower water. The stems/branches are brittle and hollow with rough ends, when crushed it emits a foul musty garlic like odor, often why it is called muskgrass or skunkweed. Sandgrass is beneficial promoting water clarity and lake bottom stabilization. During the mid summer through fall, walleyes and perch will be found on sandgrass flats.
Water Temperature:
Temperature of the water is important because of its affect on water chemistry and thermal stratifications. Chemical reactions during higher temperatures increase the biological activity. Fish, aquatic insects, zooplankton and other aquatic species all have preferred temperature ranges. As temperatures get too far above or below this preferred range, the number of individuals of the species decreases until finally there are few, or none. Another important example of the effects of temperature on water chemistry is its impact on oxygen. Warm water holds less oxygen than cool water. The temperature preferences of common game fish are shown below, but fish are not always found in water of the preferred temperature. If food is more abundant in warmer or cooler water that’s where fish will be located. · Bluegill 73-77
· Brook Trout 52-56
· Brown Trout 57-61
· Bullhead, Brown 74-78
· Carp 75-84
· Channel Catfish 74-78
· Crappie 68-73
· Chinook Salmon 53-55
· Coho Salmon 54-55
· Flathead Catfish 80-85
· Lake Trout 48-52
· Largemouth Bass 71-76
· Muskellunge 63 -67
· Northern Pike 62-71
· Rainbow Trout 56-62
· Smallmouth Bass 68-72
· Steelhead 58-60
· Stripped Bass 70-74
· Walleye 67-72
· White Bass 74-78
· Yellow Perch 66-70Oxygen:
Fish and other aquatic organisms require oxygen to live. Fish breathe as water moves past their gills and microscopic bubbles of oxygen gas in the water called dissolved oxygen absorbs into their blood stream. Oxygen in water is produced during photosynthesis (The process in which plant life converts carbon dioxide in to oxygen during daylight hours) Other sources of oxygen include the air and inflowing streams. This is why moving waters rarely have low oxygen levels.
Seasonal Effects on Water Systems:
During each season in natural lakes, flowages, reservoirs, and ponds fish movement is keyed by two major factors: Water Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen. Throughout the year fish will inhabit the zone that is closest to satisfying both these needs. To understand the relationship that happens on water systems, it is important to know the seasonal changes that occur.
In early spring before ice-out on Northern lakes and flowages the water temperature on the bottom reaches around 39 degrees, the remaining ice melts from the sun and wind warming the surface water to 39 degrees. As the water temperature and density is consistent from top to bottom this occurrence is called “Spring Turnover” Fish may be anywhere, but will migrate to the shallows as temperatures warm and new aquatic plant growth takes place adding additional oxygen to the shallow water.
As the surface temperature rises warmer lighter surface water starts to separate from cooler heavier water below. As the water temperature increases the wind will not have an affect on mixing the water. This begins the process of Thermal Stratification on lakes, flowages and reservoirs, typically with water depths greater than 15 feet for small lakes and 30 feet for larger ones. Because of this property the water separates into layers of distinctly different density caused by differences in water temperature. Shallow lakes, rivers and streams will not stratify into layers as the entire water is mixed by the wind or current.The upper layer (epilimnion) is warmer, lighter and most buoyant water that is circulated by the wind as it renews the oxygen supply. Many game fish use and stay in this layer during the season as plant life and oxygen is abundant and as preferred temperature dictates for each specie.
Next is the middle layer (metalimnion) which includes the thermocline. This is the transition zone where the temperature drops very fast. Schooling fish will use this layer as light and oxygen is present. Finally, the lower layer (hypolimnion) which extends from the thermocline to the lake bottom. Water temperature remains constant but lack of oxygen levels in this layer may cause cold water species to suspend into the thermocline during mid to late summer.
As early fall approaches cool nights and wind will lower the surface temperature. This causes the margin between the layers epilimnion and metalimnion to be less distinct. The hypolimnion layer remains intact and without much oxygen. Fish will move shallower during this period. During mid fall the surface temperature cools even more and begins to sink. As the temperature in the mixed upper layers equals that of the hypolimnion; the wind easily mixes the entire water column causing similar temperature and density throughout thus the water temperature and dissolved oxygen will be constant in all depths. This is known as “Fall Turnover”. Fish will be scattered during this period. In late fall the water continues to cool as the surface temperature drops below 39 degrees it becomes lighter and floats over the deeper warmer water. Fish will be deeper at this time period.
With the beginning of winter early ice forms, fish may be found at any depth but will relate to first ice feeding periods in shallow water using the remaining live weeds. As ice and snow becomes thicker it reduces the sunlight, the plant life ceases starting the decaying process that consumes oxygen. Fish will remain in the mid to upper water column. In late winter as the ice and snow becomes the thickest the water will have it’s lowest oxygen content. Fish locations will be harbored around moving open water, springs or the upper layer that has the highest oxygen content.
Water Classifications:
Each water system possesses a unique “personality”. Important elements that make the basis for physical characteristics are: Water Source, Fertility, and Geographic Location. Lake water sources are classified into four types. Seepage, Groundwater, Drainage and Impoundment.
The water source and fertility is important in determining water quality, all water system levels increase from rain and decrease from evaporation. Run off (land that drains towards the lake) carries nutrients into the water providing a higher fertility level where it fuels algae blooms. Algae is the basic link in the food chain. Lakes with moderate to high fertility produces the largest fish crop. Lakes with low fertility (sterile) surrounded by rocky shorelines and nutrient poor land which inhibits algae blooms produces lower fish production.
Seepage lakes and ponds that rely on rain as there main water supply with limited water exchange (lack of stream inlets & outlets) will be susceptible to acid rain, and high mercury content. On lakes that the major water source is Groundwater or Spring fed, acid rain amounts will be diminished and will contain low to moderate fertility levels.
Drainage lakes (stream fed and drained) fertility levels are higher and water exchange rate takes place more rapidly. These lakes will have quality nutrient rich water and fish populations.
Impoundments are man made lakes, also called reservoirs and flowages created by damming a stream or river system. Most Eastern and Western reservoirs tend to be very deep (over one hundred feet) while Midwest and Southern reservoirs are shallower. Impoundments seldom lack oxygen in the depths due to water level fluctuations created by the dam causing moving water and current.Geographic Location is another indicator of water type and quality. Lakes are divided into three categories known as trophic states. Oligotrophic – Mesotrophic, and Eutrophic. These categories reflect depth, basin size, shape, nutrient and clarity levels.
Oligotrophic Waters: Mostly found in Eastern Canada and Northern States from Minnesota to Maine. Oligotrophic lakes are clear, deep and cold located in rocky geography. Sparse weed growth and lack of large algae blooms make these lakes low in nutrients. The fish populations ( cold water types: Lake Trout, Char, Northern Pike) are lower but have a food chain capable of sustaining a trophy fishery. Because of the slow growth rate due to the cold climate it is recommended that catch and release is used.
Eutrophic Waters: Predominately found in the Southern United States although there are many in the North. Eutrophic lakes are small, shallow, weedy with cloudy water and a mud basin, usually located in farm land areas where nutrient rich soil is abundant and run off causes frequent algae blooms. The fish populations ( warm water types: Bass, Sunfish. Cat Fish, Rough Fish) are vulnerable to winterkill (iceover) in the Northern States from lack of depth and oxygen.
Mesotrophic Waters: These lakes are found anywhere in North America but primarily are located in the Northern States and Southern Canada. Mesotrophic lakes are fertile with moderate weed growth, water clarity is clear to stained with the basin consisting of gravel, rock and sand. The diversity of water depths and nutrients can support cold and warm water fish populations ( Bass, Walleye, Perch, Northern Pike, Muskies, Catfish, Panfish, Trout) Considered a good fishery for multiple species.
All lakes at one time thousands of years ago formed as Oligotrophic waters (early lake life), as the aging process occurs aquatic plants and animals die, their remains form a layer of organic properties on the lake bottom. As this layer increases the lake becomes shallower allowing the sunlight to warm the water. As plant life becomes more abundant the lake moves into the Mesotrophic period (mid lake life). Eventually as the lake bottom fills from nature and the affects of man the lake will become Eutrophic (old lake life).
Ponds & Pits:
There are millions of ponds in the U.S. some are built for agricultural use, others for irrigation or erosion control. Nature provides ponds by beavers damming small streams. Most ponds are shallow and if stocked warm water fish such as Largemouth Bass and Bluegills are present.
Pits are results from strip mining, gravel pits and quarries that fill with water after their operations cease. Generally pits are much deeper than ponds in some cases over 500 feet. Pits can hold a wide specie range of fish; deep cold water pits: (Trout and even Salmon) shallower pits: (warm water Bass, Catfish, Crappies, and Bluegills). ![Underwater World of Freshwater Fish]()
Rivers & Streams:
North America is blessed with an abundance of flowing water. There are 3.24 million miles of river and streams in the U.S. alone – enough to circle the world 130 times. Rivers begin rather unpretentiously. They are lazy. They follow the force of gravity until they find the most convenient way to flow downhill. This is governed by the topography of the area in which they flow. In time, the river begins to modify this landscape until it creates a valley. The average river system, if viewed from above, looks like a many branching tree. Hundreds, perhaps thousands, of small rivulets flow into slightly larger branches, which in turn flow into tributaries. Eventually the water makes its way into the main body of the river, flowing to its final destination a lake or sea.
All freshwater species live or utilize rivers and streams. Ocean run Salmon travel miles up a river to spawn from which they where born. Walleyes and White Bass make spring “runs” to their spawning grounds. Water temperature is a major factor for spawning and what species inhabit the river.Cold water streams and rivers will be best suited for Trout, Steelhead, Salmon and Grayling. Warm water streams and rivers are home to Bass, Walleyes, Catfish, and Carp.
When fishing a stream or river the mechanics of moving water (current) provides structure and cover as in a lake with weeds, cribs, and rock bars. Most rivers and streams have riffle-run-pool fish holding habitat.
Riffles: Known as rapids, shallow fast moving water over rocks rubble and boulders. Small minnows and game fish use this area for protection from predators. Large gamefish will feed in this area during dusk and dawn.
Runs: This section follows the riffle (rapids) current is slower than the rapids and not as turbulent. As the current flows it excavates a deeper channel as it slows it circulates forming a pool.Pools: Also known as holes, this is the deepest area of the river or stream. A major fish holding area.
Plunge Pools: Located at the base of dams or waterfalls. As water falls it erodes the base of the stream or river creating a dug out. This is also an excellent fish holding area for feeding as food is presented from the force of the current.Eddies: Any land point, island, sharp bend,large boulder or obstacle such as logs or bridge pilings that reduces the current. Eddies form upstream and downstream. Fish will stage in front of and back of a eddie, always work both.
Undercuts: As rivers and streams have bends, turns, and oxbows the current flowing will increase on the outside bend and on slow in the inside. This forms undercuts along the shoreline that will hold fish.
 In keeping with Penn tradition, the new Spinfisher V series of reels give the impression they’re indestructible.
In keeping with Penn tradition, the new Spinfisher V series of reels give the impression they’re indestructible. nd four and five-inch soft baits produced plenty of 1.5 to 2kg Waitemata snapper, kahawai and trevally, plus a bunch of gurnard in the Kaipara Harbour. I also used the reel in combination with other rods for non-softbait fishing styles as already mentioned.
nd four and five-inch soft baits produced plenty of 1.5 to 2kg Waitemata snapper, kahawai and trevally, plus a bunch of gurnard in the Kaipara Harbour. I also used the reel in combination with other rods for non-softbait fishing styles as already mentioned.
















 Floating plants are not rooted and are free to move about the water’s surface. The main habitat for floating plants are backwater areas on rivers and streams where the current slackens and protected bays on lakes and flowages. In limited water movement area’s floating plants can be mixed in with other emergent and submerged plants forming what is commonly called “slop” by creating a surface mat that attracts largemouth bass, in deeper waters slop will hold northern pike and muskie. Fishing slop is extremely fun when the fish are on and you have the right set-up and lures. Fishing the slop requires heavy tackle and line to horse the fish out of cover. Baitcasting reels spooled with low stretch 17lb to 30lb test line, rods rated heavy with fast action are recommended. Lure choices include weedless soft plastics, worms and lizards using heavy sinkers to penetrate the thick vegetation, top water frog and rat imitations are excellent for surface slop fishing, there is nothing more exciting when a bass explodes on one of these. The common North American native floating plants are Duckweed, Bladderwort and Watermeal.
Floating plants are not rooted and are free to move about the water’s surface. The main habitat for floating plants are backwater areas on rivers and streams where the current slackens and protected bays on lakes and flowages. In limited water movement area’s floating plants can be mixed in with other emergent and submerged plants forming what is commonly called “slop” by creating a surface mat that attracts largemouth bass, in deeper waters slop will hold northern pike and muskie. Fishing slop is extremely fun when the fish are on and you have the right set-up and lures. Fishing the slop requires heavy tackle and line to horse the fish out of cover. Baitcasting reels spooled with low stretch 17lb to 30lb test line, rods rated heavy with fast action are recommended. Lure choices include weedless soft plastics, worms and lizards using heavy sinkers to penetrate the thick vegetation, top water frog and rat imitations are excellent for surface slop fishing, there is nothing more exciting when a bass explodes on one of these. The common North American native floating plants are Duckweed, Bladderwort and Watermeal.


 This plant is known to anglers as cabbage and has over 50 varieties in North America. Cabbage is both a deep and shallow water weed that has broad leaves and a brittle stems. They vary in colors from brownish red called tobacco cabbage to a light green leaf. Cabbage is the preferred choice of many large game fish and the most productive. Cabbage is also known as pike weed, muskie weed, and celery.
This plant is known to anglers as cabbage and has over 50 varieties in North America. Cabbage is both a deep and shallow water weed that has broad leaves and a brittle stems. They vary in colors from brownish red called tobacco cabbage to a light green leaf. Cabbage is the preferred choice of many large game fish and the most productive. Cabbage is also known as pike weed, muskie weed, and celery. Coontail or also know as hornwort, is a dark olive green bushy submerged perennial plant that grows in clumps or dense colonies that forms a canopy type cover in shallow water. The tips of branches are crowded with leaves giving it a “coontail” appearance. The submerged colonies of coontail provides excellent habitat and cover for bait fish as well as other wildlife species (e.g. amphibians, reptiles, ducks, etc.)which attracts most predator game fish. The fruits of coontail are consumed by ducks and it is considered a good wildlife food.
Coontail or also know as hornwort, is a dark olive green bushy submerged perennial plant that grows in clumps or dense colonies that forms a canopy type cover in shallow water. The tips of branches are crowded with leaves giving it a “coontail” appearance. The submerged colonies of coontail provides excellent habitat and cover for bait fish as well as other wildlife species (e.g. amphibians, reptiles, ducks, etc.)which attracts most predator game fish. The fruits of coontail are consumed by ducks and it is considered a good wildlife food. Eelgrass is a rooted shallow water plant found in flowing water. It has long, thin, ribbon-like leaves (1/2 – 3/4 inches wide) that are commonly 3 to 4 feet long. The vein pattern in the leaves of eelgrass is very distinctive and resembles celery. Eelgrass forms dense colonies dominating other submerged plants to grow. The submerged portions of eel grass provides dense underwater structure as an excellent habitat for bait fish and invertebrates. Northern pike and bass favors eelgrass during the summer months. Other common names include: Tape grass and wild celery.
Eelgrass is a rooted shallow water plant found in flowing water. It has long, thin, ribbon-like leaves (1/2 – 3/4 inches wide) that are commonly 3 to 4 feet long. The vein pattern in the leaves of eelgrass is very distinctive and resembles celery. Eelgrass forms dense colonies dominating other submerged plants to grow. The submerged portions of eel grass provides dense underwater structure as an excellent habitat for bait fish and invertebrates. Northern pike and bass favors eelgrass during the summer months. Other common names include: Tape grass and wild celery.



 Filamentous algae are multi-celled that form into a mat of long chains or threads called filaments that resembles wet wool. Filamentous algae starts growing along the bottom in shallow water appearing fur-like, attaching to rocks, drowned wood, and other aquatic plants. As the production of oxygen increases it will float to the surface forming large mats, known as “Pond Scum.” Filamentous algae has no direct food value to wildlife.
Filamentous algae are multi-celled that form into a mat of long chains or threads called filaments that resembles wet wool. Filamentous algae starts growing along the bottom in shallow water appearing fur-like, attaching to rocks, drowned wood, and other aquatic plants. As the production of oxygen increases it will float to the surface forming large mats, known as “Pond Scum.” Filamentous algae has no direct food value to wildlife. Chara is the most advanced plant of the algae family though often confused with submerged plants. Chara commonly know as “sandgrass” is gray-green, branched with no root system, it grows in short thick mats, covering the lake bottom like a carpet. It can grow to depths of 30 feet, but is more common in shallower water. The stems/branches are brittle and hollow with rough ends, when crushed it emits a foul musty garlic like odor, often why it is called muskgrass or skunkweed. Sandgrass is beneficial promoting water clarity and lake bottom stabilization. During the mid summer through fall, walleyes and perch will be found on sandgrass flats.
Chara is the most advanced plant of the algae family though often confused with submerged plants. Chara commonly know as “sandgrass” is gray-green, branched with no root system, it grows in short thick mats, covering the lake bottom like a carpet. It can grow to depths of 30 feet, but is more common in shallower water. The stems/branches are brittle and hollow with rough ends, when crushed it emits a foul musty garlic like odor, often why it is called muskgrass or skunkweed. Sandgrass is beneficial promoting water clarity and lake bottom stabilization. During the mid summer through fall, walleyes and perch will be found on sandgrass flats.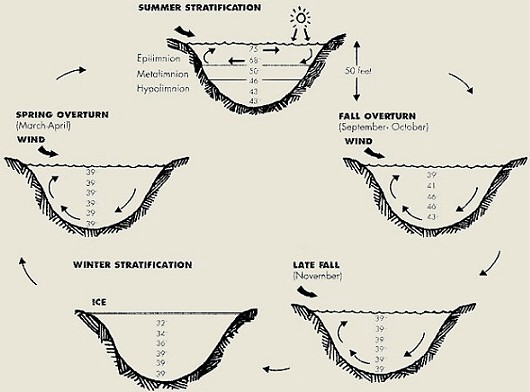




 As the colder months are approaching and hats and scarfs are hung back onto the coat rack, immune boosting herbs and cold remedies find their place back onto the shelves of our green medicine cabinets as well.
As the colder months are approaching and hats and scarfs are hung back onto the coat rack, immune boosting herbs and cold remedies find their place back onto the shelves of our green medicine cabinets as well. 
 You can make your own propolis products from raw propolis very easily. The best source of propolis is – your local beekeeper! The best way to meet him or her is to look up your local bee club online (there is always a local beekeeper club) and go to one of their meetings. They will be delighted to welcome a newcomer and will love to share their passion with you. The majority of beekeepers have no use for propolis and throw it away after collection. Most likely somebody will gift you a chunk or you can buy a few ounces at a reasonable price.
You can make your own propolis products from raw propolis very easily. The best source of propolis is – your local beekeeper! The best way to meet him or her is to look up your local bee club online (there is always a local beekeeper club) and go to one of their meetings. They will be delighted to welcome a newcomer and will love to share their passion with you. The majority of beekeepers have no use for propolis and throw it away after collection. Most likely somebody will gift you a chunk or you can buy a few ounces at a reasonable price. 






















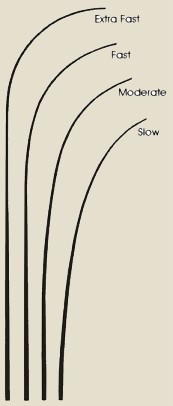 Action refers to the flex characteristics of a rod, in other words how much the rod bends when you put pressure on the tip and how far the rod flexes. Action ranges from extra fast where just the tip flexes to slow or softer where the majority of the rod flexes. Fast action rods are the best choice when the fishing technique requires the sensitivity of feeling light biting fish or when fishing for large game fish in heavy cover and weeds where the key is to setting the hook fast with just a snap of the wrist moving the fish’s head up and away. For instance, fast action light rods are used for jigs, soft plastic worms or twitching minnow/shad shaped crank baits for bass and walleye. Heavier fast action rods are used for Muskies & Pike in burning bucktails, walking top water lures or a cadence retrieve on gliders and jerkbaits. The moderate action rod is the most common choice due to the versatility of fishing applications, in casting a moderate action rod it will bend for about half of it’s length which will provide more casting distance and still have the capability for a adequate hookset. Ideal for slip bobbers/floats live bait for walleye fishing because the fish is less likely to feel resistance from the soft tip and drop the bait, along with reaction lures such as crank baits, spinner baits and spoons for bass and pike where the slower action will not pull the lure out of the fish’s mouth. Slow or Soft Action rods will bend starting in the lower third using nearly the entire rod providing the most flexibility. Because of this parabolic action the angler is using the rod as a shock absorber in fighting the fish, this allows the use of very light line. These rods are used for panfish especially for the paper thin mouths on crappies so the hook is not ripped clear on hooksets, and are also popular for drift fishing spawn sac’s on trout and salmon streams.
Action refers to the flex characteristics of a rod, in other words how much the rod bends when you put pressure on the tip and how far the rod flexes. Action ranges from extra fast where just the tip flexes to slow or softer where the majority of the rod flexes. Fast action rods are the best choice when the fishing technique requires the sensitivity of feeling light biting fish or when fishing for large game fish in heavy cover and weeds where the key is to setting the hook fast with just a snap of the wrist moving the fish’s head up and away. For instance, fast action light rods are used for jigs, soft plastic worms or twitching minnow/shad shaped crank baits for bass and walleye. Heavier fast action rods are used for Muskies & Pike in burning bucktails, walking top water lures or a cadence retrieve on gliders and jerkbaits. The moderate action rod is the most common choice due to the versatility of fishing applications, in casting a moderate action rod it will bend for about half of it’s length which will provide more casting distance and still have the capability for a adequate hookset. Ideal for slip bobbers/floats live bait for walleye fishing because the fish is less likely to feel resistance from the soft tip and drop the bait, along with reaction lures such as crank baits, spinner baits and spoons for bass and pike where the slower action will not pull the lure out of the fish’s mouth. Slow or Soft Action rods will bend starting in the lower third using nearly the entire rod providing the most flexibility. Because of this parabolic action the angler is using the rod as a shock absorber in fighting the fish, this allows the use of very light line. These rods are used for panfish especially for the paper thin mouths on crappies so the hook is not ripped clear on hooksets, and are also popular for drift fishing spawn sac’s on trout and salmon streams.